
General Business

January 8, 2020
ISO 9001 - Clause 5: Leadership and commitment explained
Leadership is a skill which involves motivating a group of individuals to work towards a common goal. In a business setting, this involves leading and guiding staff and colleagues with a strategy or a plan to meet the business needs of the company.
ISO 9001 Clause 5 also stresses on the above and the clause is all about leadership’s role in the quality management system. To put in simple words, Leaders need to ‘walk the talk’ to achieve the benefits of the quality management system. They need to ensure Quality Management System and the business processes are operating together to achieve the desired objectives and to bring in unity of purpose.
Why Is it important?
The role of a leader is paramount when taking any new initiative in an organisation. Many process improvements fail when leaders do not take active participation and don’t lead it from the front. That is why ISO 9001 emphasises on this clause which ensures that the leader's role is understood well and they take charge of the quality management system and its results. Another important reason for the involvement of leadership is to bring the quality management system closer to business. Leaders when they directly get involved in the effectiveness of the QMS ensures that quality is an integral part of the business and each person takes it as seriously as the leader does. This requires motivation and encouragement to support and improve processes and no other than a Leader can do this efficiently. Additionally, ISO 9001 lays a lot of emphasis on risk-based thinking, establishing internal/external issues, requirements of interested parties and planning the QMS around it. (Refer link to Clause 4 article). That makes it important for the top management to be involved in all stages of establishing and maintaining the QMS.
Leadership and Commitment
Quality Management System implementation cannot be successful without leadership commitment towards it. Leadership needs to believe in the system themselves; only then they can ensure that their teams understand its importance and benefits clearly. Here are some of the guidelines defined by ISO 9001 in Clause 5 on the role of the top management is leading this initiative. Top Management shall:
- Take accountability and responsibility for the effectiveness of the Quality Management System and ensure that it meets its purpose
- Based on the context and strategic direction of the organization, ensure that Quality policies and objectives are established for the Quality Management System.
- Ensure that the Quality Management System works together with the organisation’s business processes; This will in-turn ensure that the requirements of the customer are met and this enhances customer experience.
- Promote process approach. This is where top management’s own commitment and understanding on the principles of QMS is required so that they imbibe these principles in their working and encourage use of processes across the organization.
- Communicate the importance of conforming to the QMS and its requirements.
- Provide adequate resources needed for the QMS; Top Management needs to create effective organizational structures and provide right internal environment that motivates people towards achievement of organisation’s goals and objectives.
- Engage, direct and support persons to contribute to the effectiveness of the Quality Management System. This requires top management’s direct involvement in all stages of QMS including planning, reviewing the results and suggesting improvements. The top management needs to show commitment towards processes to motivate others also to implement and improve processes.
- Promote a culture of process improvements, take initiatives to develop new products and introduce new tools, to improve efficiency and productivity.
- Support other relevant management roles to ensure that all roles as required for effective implementation of QMS are available in the organization.
- Maintain a consistent focus on customer requirements, meeting of regulatory or statutory requirements and enhancing customer satisfaction. All the requirements shall be determined and met and confirming products or services provided to the customer.
- Determine and address any risks that may hinder an organization’s ability to provide conforming products/services, or which may have a negative effect on customer satisfaction.
Quality Policy
The first step for establishing the Quality Management System is to define the quality policy and quality objectives. The intent of the Quality policy is to provide top management’s vision on quality management of the organization. Quality Policy is a way through which top management can project its commitment towards quality to internal as well as external stakeholders.
The Quality Policy should capture the purpose and context of the business and provide a framework for setting up Quality objective. The Quality Policy should specify your commitment to ‘satisfy applicable requirements’ and ‘continually improve the effectiveness of your QMS’.
An example of a Quality Policy for a Training institute is given below:
‘ABC training is committed to providing high-quality services to our customers that meet the customer’s requirements and other statutory and regulatory requirements while maintaining profitability and competitiveness.
ABC training constantly strives toward continual improvement and higher customer satisfaction.’
The quality policy represents the organizations’ core values and it strengthens the company’s commitment towards quality; it is important that it is understood well within the organization and each employee is aware of the quality policy. This can be achieved when the quality policy is documented, communicated and understood within the organization.
It can be made available on your website, your employee handbook/quality manual or displayed at various locations in the office so that employees read and imbibe its values in day to day work. It can also be made available when onboarding new employees and made part of the onboarding process. It is also important to make the quality policy available to external interested parties, like customers/suppliers, etc. This can be done through your website/marketing material or communicated through emails, whenever requested.
Quality Policy shall be reviewed periodically by top management based on changes in the context of the organisation. This can be done during management reviews.
Organizational roles, responsibilities and authorities
This sub-clause of ISO 9001 requires that the top management provide adequate resources and assign responsibilities and authorities necessary to implement QMS effectively. A simple method of doing this is to define the organizational structure and associated hierarchies. Various methods like job descriptions, organization maps/ charts, procedures, work instructions, etc can be used to define organizational structure and responsibilities within the organisation. A sample organization chart of a small training institute is given below:
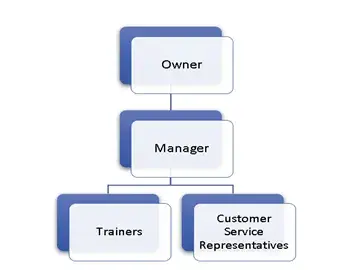
The intent of the clause is to ensure that each employee understands their role with respect to the implementation and reporting of elements of the QMS and maintain focus on customer requirements. Job Descriptions is an easy mechanism through which you can specify what trainings, qualifications and experience each job roles requires. This will help you in getting the right candidates while hiring for a position and also ensure that the employee is clear on the job requirements and his /her responsibilities.
These organization structures/ role and responsibilities need to be communicated and deployed throughout the organisation via orientation programs, training, meetings or through procedures or work instructions.
Additionally, the top management needs to continuously work towards optimizing the processes and bringing in changes and improvements to the QMS. Employees shall be encouraged to also suggest opportunities for improvements and the top management shall ensure that integrity of QMS is maintained when these changes are planned and carried out.